Part A Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each from CHEM 4600 at Nova Southeastern UniversityNames of Nucleotides DKosig / Getty Images The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively The name of the baseDNA complementary base pairing Aug 04, Complementary base pairing refers to the structural pairing of nucleotide bases in deoxyribonucleic acid, which is commonly known as DNA DNA is made up of four nucleotide bases, each of which pairs with only one of the other bases The four nucleotide bases in DNA are guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine complementary base pairing

Complementarity Molecular Biology Wikipedia
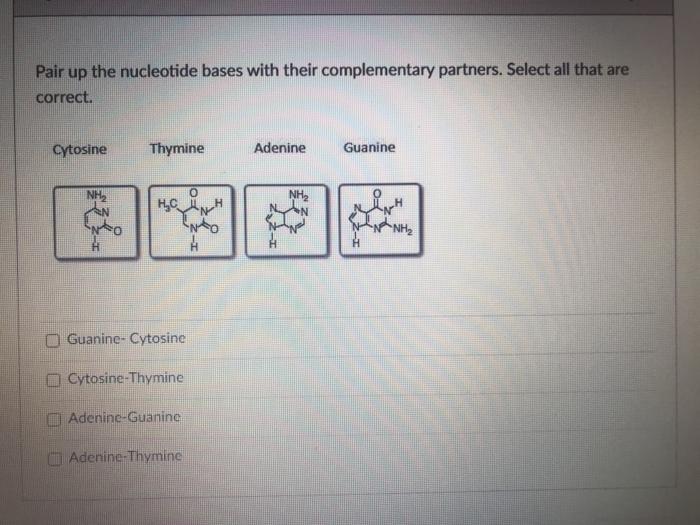
Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners masteringbiology
Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners masteringbiology-Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners masteringbiology Avala's answer may not be clear,depending on what your level of knowledge is DNA is built of 4 basic chemical units called nucleotides, which based on their chemical names we denote A,C, G, and T They are able to form a long string of any part A codon consists of _____ bases and specifiesQuestion Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners This problem has been solved!




The Influence Of Base Pair Tautomerism On Single Point Mutations In Aqueous Dna Interface Focus
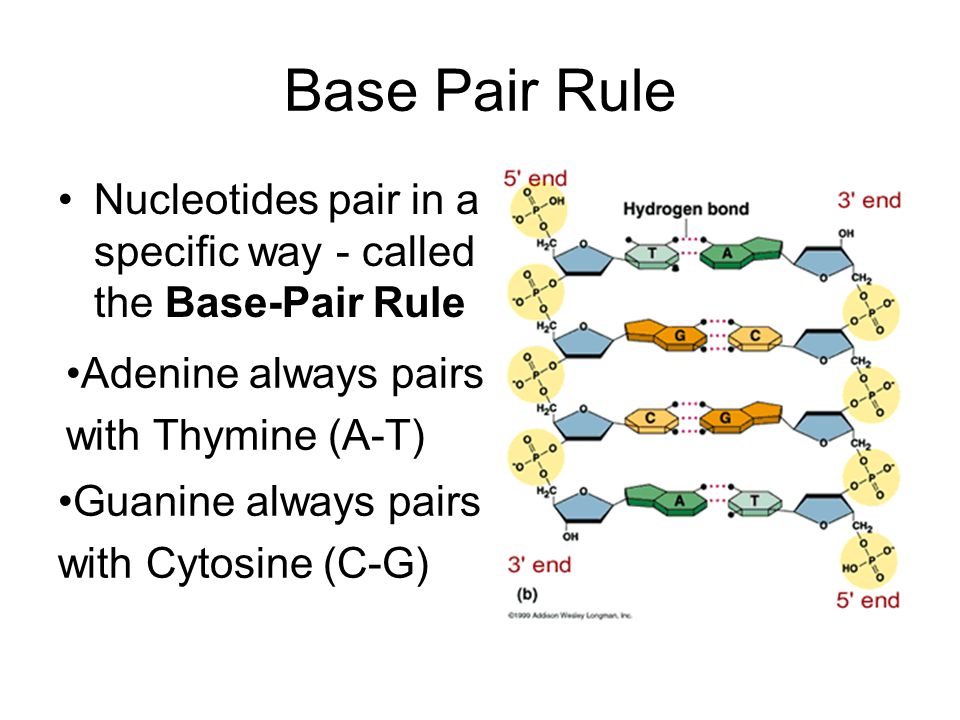
The 4 DNA Bases and Their Strict Pairing Rules The DNA of all the living beings is composed of just four bases ie Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), and Cytosine The various juxtapositions of these 4 bases give rise to the genetic codes of all the biota on the planet Know more about these DNA bases in this postPair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each Item to the appropriate bin Learn this topic by watching Nucleic Acids Concept Videos 2 A nucleotide is made of three parts a phosphate group, a five carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base Slide 9 3 In a single strand of DNA, the phosphate group binds to the sugar of the next nucleotide Slide 5 4 Human answered by gaurav96 (23,778 points) In a DNA sequence, the purine adenine always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine, and the purine guanine always pairs with the pyrimidine cytosine
5′ CAGTCAAGCAT 3′ Drag and drop each base to match with its partner in order to maximize hydrogen bonding Adenine and thymine are complementary and join via two hydrogen bonds Guanine and cytosine are complementary and join via three hydrogen bonds Complementary base pairing refers to the structural pairing of nucleotide bases in deoxyribonucleic acid, which is commonly known as DNA DNA is made up of four nucleotide bases, each of which pairs with only one of the other bases The four nucleotide bases in DNA are guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymineBase pairs that form stable connections are called complementary bases Consistent pairings of complementary bases allow cells to make doublestranded DNA from a single strand template, create messenger RNA from DNA and synthesize proteins from individual amino acids by matching nucleotides bases on messenger RNA with their complementary bases on transfer RNA The
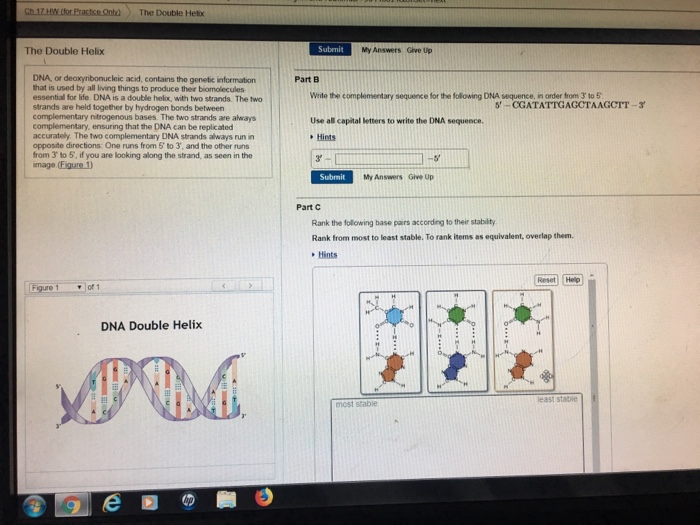
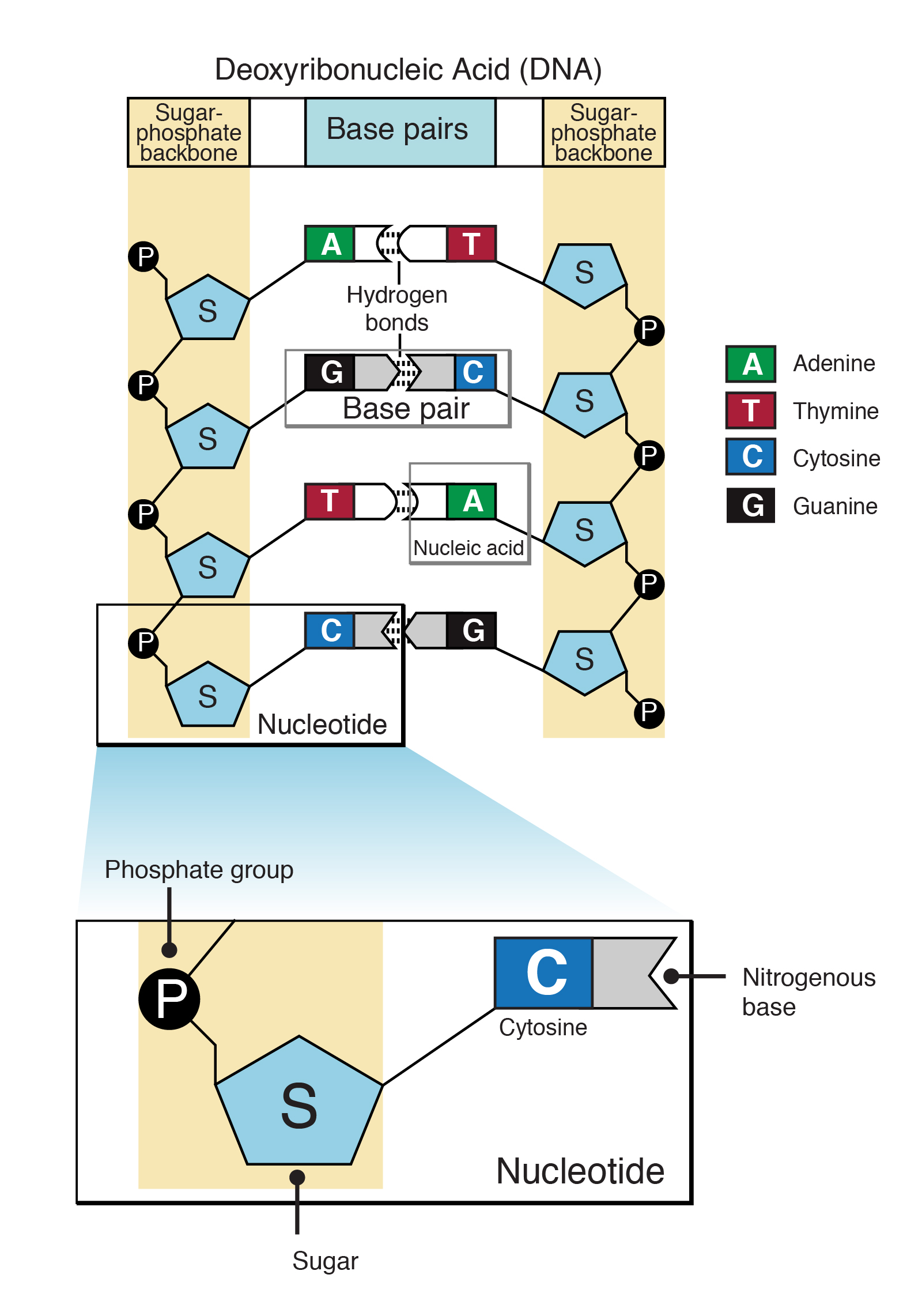
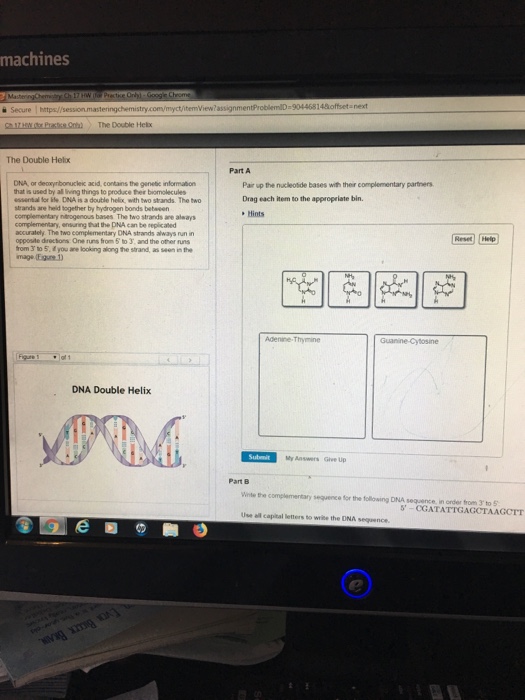
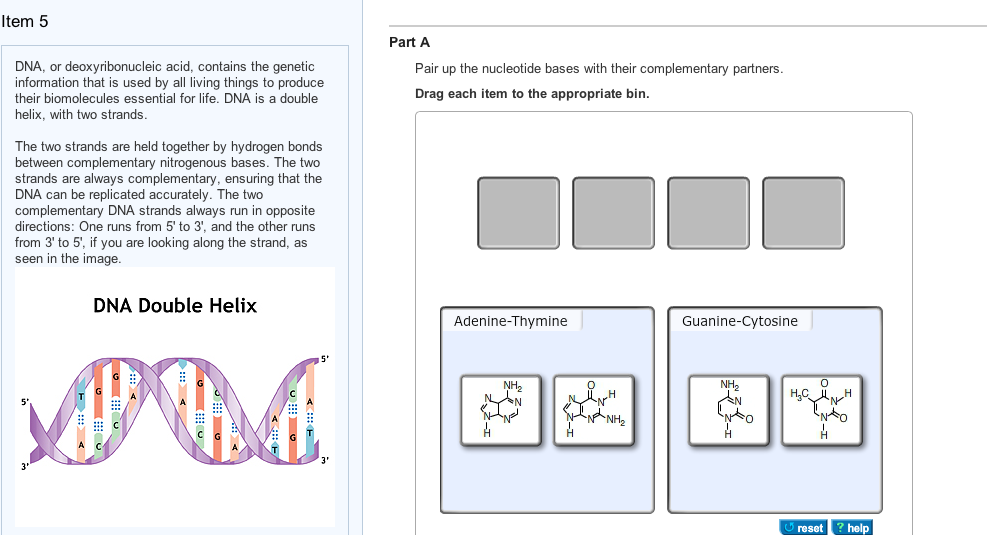
DNA is a double helix, with two strands The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogenous bases The two strands are always complementary, ensuring that the DNA can be replicated accuratelyA nitrogenous (nitrogencontaining) base;Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Tech News Rosalind Franklin Beyond the Double Helix The Developer Labs 1 Comment a phosphate group, a strand of dna contains the bases adenine, an okazaki fragment has which of the following arrangements, and guanine, are _____, cytosine, in that order which would be the order of the bases




Mb Ch 5 Pt 2 Adaptive Follow Up Set 3 Flashcards Quizlet



Www Mdpi Com 75 1729 10 12 346 Pdf
A nitrogenous base is an organic molecule that contains the element nitrogen and acts as a base in chemical reactions The basic property derives from the lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom The nitrogen bases are also called nucleobases because they play a major role as building blocks of the nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid () These nucleotides are complementary —their shape allows them to bond together with hydrogen bonds In the CG pair, the purine (guanine) has three binding sites, and so does the pyrimidine (cytosine) The hydrogen bonding between complementary bases is what holds the two strands of DNA together Click here to know more about it Just so, which of the following DNA base pairs is complementary? DNA is a type of nucleic acid made up of many subunits called nucleotides Each nucleotide has three parts a 5carbon ribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base Two complementary strands of DNA come together thanks to hydrogen bonding between the nitrogenous bases that allows DNA to make a ladderlike form that twists into the famous double




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners




Cognate Base Pair Selectivity Of Hydrophobic Unnatural Bases In Dna Ligation By T4 Dna Ligase Kimoto 21 Biopolymers Wiley Online Library
The two complementary DNA strands always run in opposite directions One runs from 5' to 3', and the other runs from 3' to 5', if you are looking along the strand, as seen in the image DNA Double Helix Part A Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each item to the appropriate binPair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each Item to the appropriate bin Each nucleotide base can hydrogenbond with a specific partner base in a process known as complementary base pairing Cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine, and adenine forms two




5 12 Png Part A Q 12 Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Drag Each Item To The Appropriate Bin View Available Hint S Reset Course Hero




Complementary Nucleotide Bases Science Primer
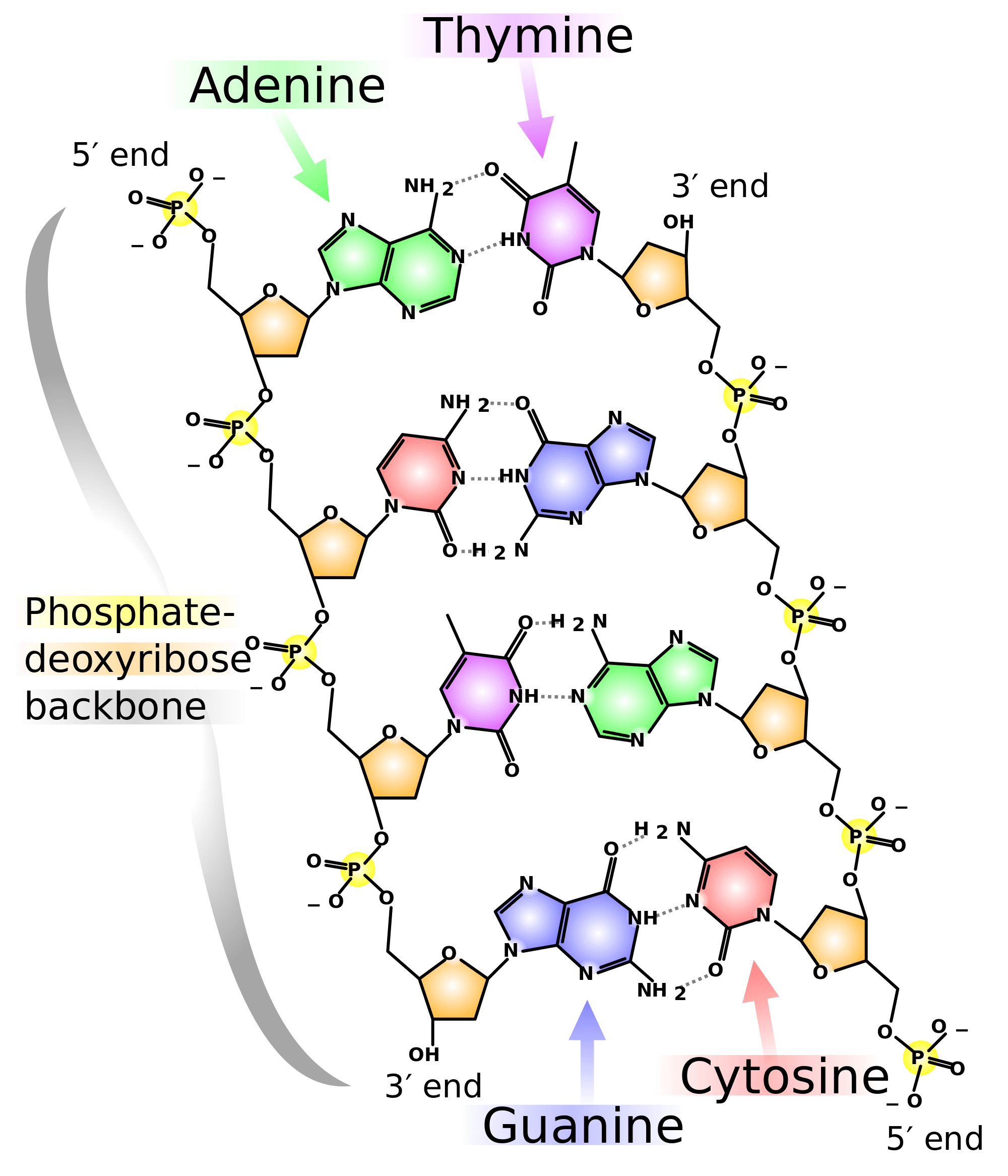
Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Loading Published On photograph Exam 3 Chs 5 (DNA Structure and Replication Machinery photograph Biology Archive Cheggcom photograph Solved Shown In The Picture, The Nucleotide Bases And Com photograph Print Exam 3 Chs 5 (DNA Structure and Replication photograph nucleotide basesThis is because their nucleotide bases can bond to other bases in more than one direction, If each nucleotide pairs vertically with its partner (C to G, A to T, etc), then the result is the complementary sequence CTAATCT This process is called template matching or basepairing or sometimes WatsonCrick pairing, after the discoverers of DNA's structure The originalIn a DNA molecule, the G–C base pair is linked by two hydrogen bonds, and the A–T base pair is linked by three hydrogen bonds They always pair up in a particular way, called complementary base pairing These basic units are linked together to form strands by strong bonds between the deoxyribose sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next nucleotide The bond



Q Tbn And9gcrjf0l5uokcrcok3d4qc3yacgpwma1frzyovpmplnemumzfwofm Usqp Cau




5 12 Png Part A Q 12 Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Drag Each Item To The Appropriate Bin View Available Hint S Reset Course Hero
See the answer Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partnersThey always pair up in a particular way, called complementary base pairing thymine pairs with adenine (TA) guanine pairs with cytosine (GC) ThesePart A Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each from BIOL 4103 at University of Houston




How Many Base Pairs Are There If 100 Nucleotides Are Present Quora




Base Pairs Definition Types Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high 96% (8 ratings) Transcribed image text Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Each nucleotide base can hydrogenbond with a specific partner base in a process known as complementary base pairing Cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine, and adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine These hydrogenbonded nitrogenous bases are often referred to as base pairs1 decade ago Favorite Answer There are four nucleotide bases adenine (A), which always binds to thymine (T) , and cytosine , which always binds to guanine (G) What is the purpose of school rn when i literally am looking up all the answers on Google to answer In a DNA sequence, the purine




Mb Ch 5 Pt 2 Adaptive Follow Up Set 3 Flashcards Quizlet




Base Pairing
Q Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each Item to the appropriate bin Drag each Item to the appropriate bin Q Sort these nucleotide building blocks by their name or classification Each nucleotide base can hydrogenbond with a specific partner base in a process known as complementary base pairing Cytosine forms three hydrogen ;The dNTPs pair up opposite their complementary base partner (adenine pairs with thymine ;This complementary base pairing allows cells to copy information from one generation to another and even find and repair damage to the information stored in the sequences The degree of complementarity between two nucleic acid strands may vary, from complete complementarity (each nucleotide is across from its opposite) to no complementarity (each nucleotide is not across



Machines Secure Assigr The Double Helx The Double Chegg Com




Dna Base Pairs Overview Structure Expii
Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Loading Published On photograph Solved Shown In The Picture, The Nucleotide Bases And Com photograph Solved Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complement photograph Exam 3 Chs 5 (DNA Structure and Replication Machinery photograph Print Exam 3 Chs 5They always pair up in a particular way, called complementary base pairing thymine pairs with adenine (TA) guanine pairs with cytosine (GC) These Each nucleotide is a polymer made up of three parts A fivecarbon sugar (2'deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA) A phosphate molecule;




Bsc 10 Ch 16 17 18 Review Flashcards Quizlet




Mb Ch 5 Pt 2 Adaptive Follow Up Set 3 Flashcards Quizlet
Part A Late Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each item to the appropriate bin ading i Hints Reset Help AdenineThymine Submit My Answers Give Up 0709 AM




5 4 Base Pairing In Dna And Rna Biology Libretexts




Nitrogenous Base An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



1



Structure Of Nucleic Acids Bases Sugars And Phosphates Sparknotes




Dna Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Complementary Base Pairing Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Transcriptional Processing Of An Unnatural Base Pair By Eukaryotic Rna Polymerase Ii Nature Chemical Biology



Nucleotide



Print Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards




Nitrogenous Base An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Get Answer Part A Late Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Transtutors




Complementarity Molecular Biology Wikipedia



Machines Secure Assigr The Double Helx The Double Chegg Com
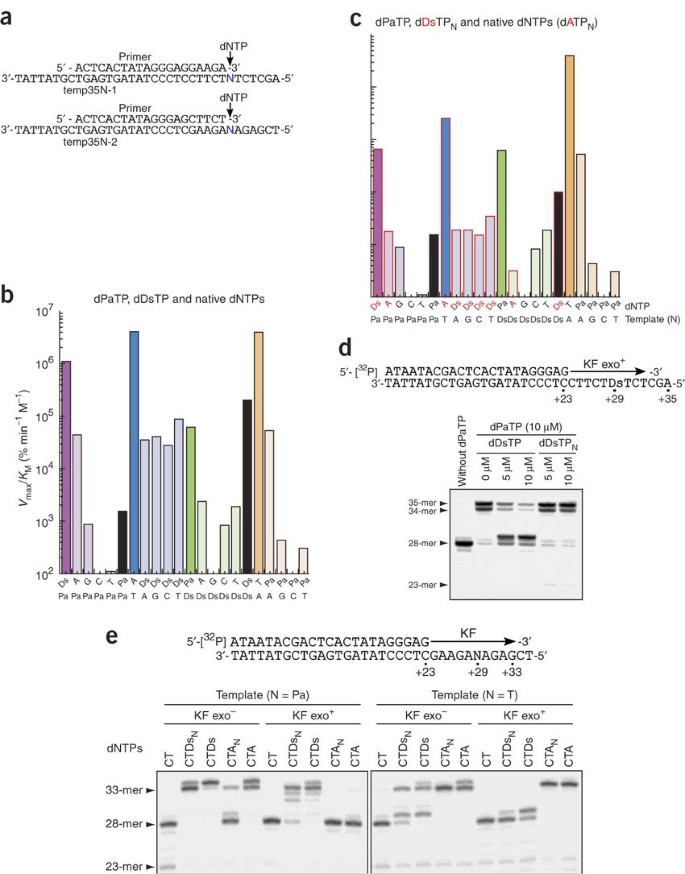



An Unnatural Hydrophobic Base Pair System Site Specific Incorporation Of Nucleotide Analogs Into Dna And Rna Nature Methods




Stronger Base Pairing Improves Dna Analyses
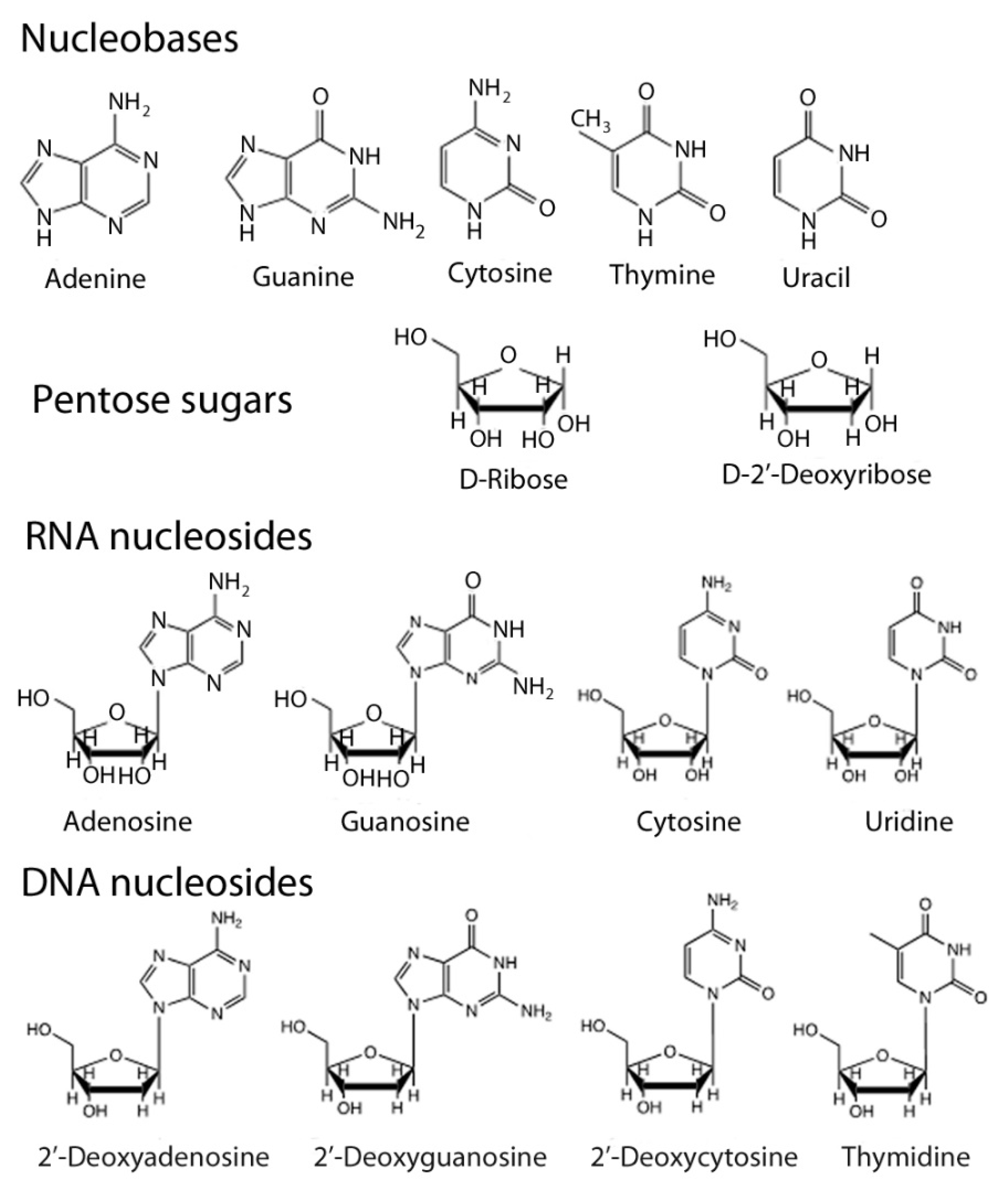



Life Free Full Text De Novo Nucleic Acids A Review Of Synthetic Alternatives To Dna And Rna That Could Act As Bio Information Storage Molecules Html
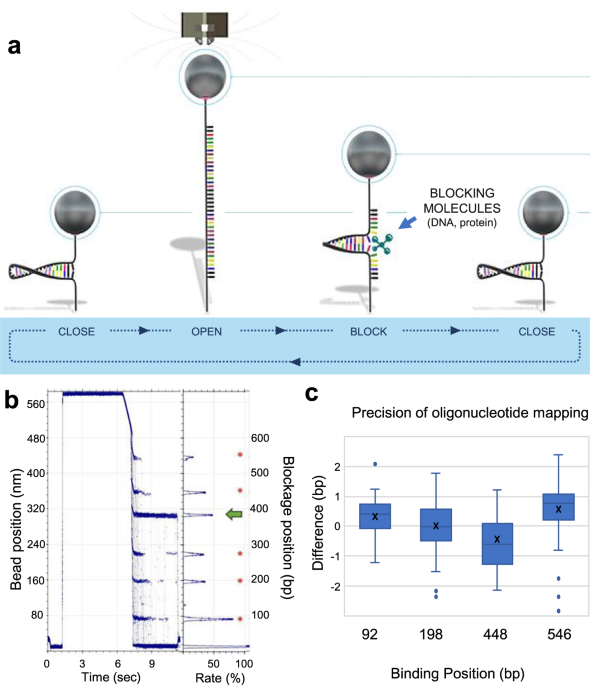



Detection Of Genetic Variation And Base Modifications At Base Pair Resolution On Both Dna And Rna Communications Biology




The Influence Of Base Pair Tautomerism On Single Point Mutations In Aqueous Dna Interface Focus




Bsc 10 Ch 16 17 18 Review Flashcards Quizlet




Base Pairs



Structure Of Nucleic Acids Bases Sugars And Phosphates Sparknotes



Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Chegg Com




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep




Biochemistry Chapter 4 Hw Flashcards Quizlet




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners



Dna Base Pairs Overview Structure Expii



Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Chegg Com




Dna Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Complementary Base Pairing Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Dna Base Pairs Overview Structure Expii



Life Free Full Text De Novo Nucleic Acids A Review Of Synthetic Alternatives To Dna And Rna That Could Act As Bio Information Storage Molecules Html




Nitrogenous Base An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



1




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners




Dna Base Pairs Overview Structure Expii



Structure And Composition Ppt Video Online Download



Acgt




19 2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics Of General Organic And Biological Chemistry
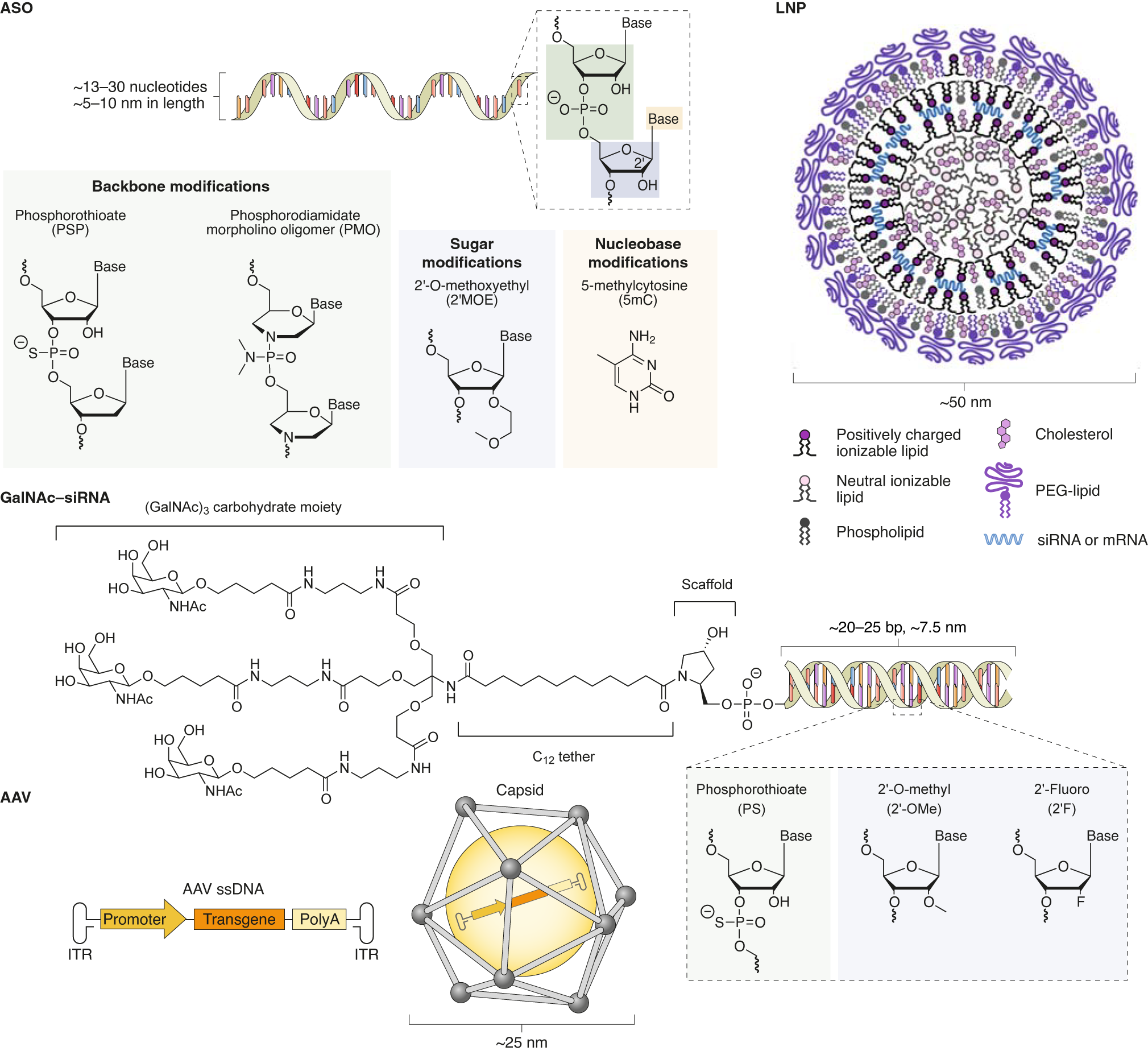



The Current Landscape Of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Nature Nanotechnology




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners




Bsc 10 Ch 16 17 18 Review Flashcards Quizlet
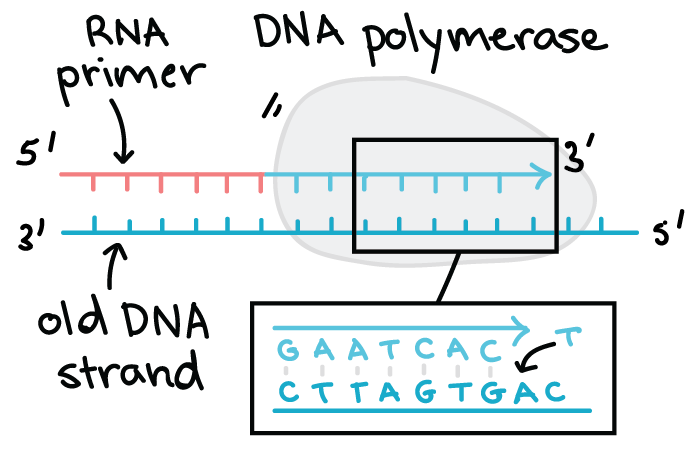



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy
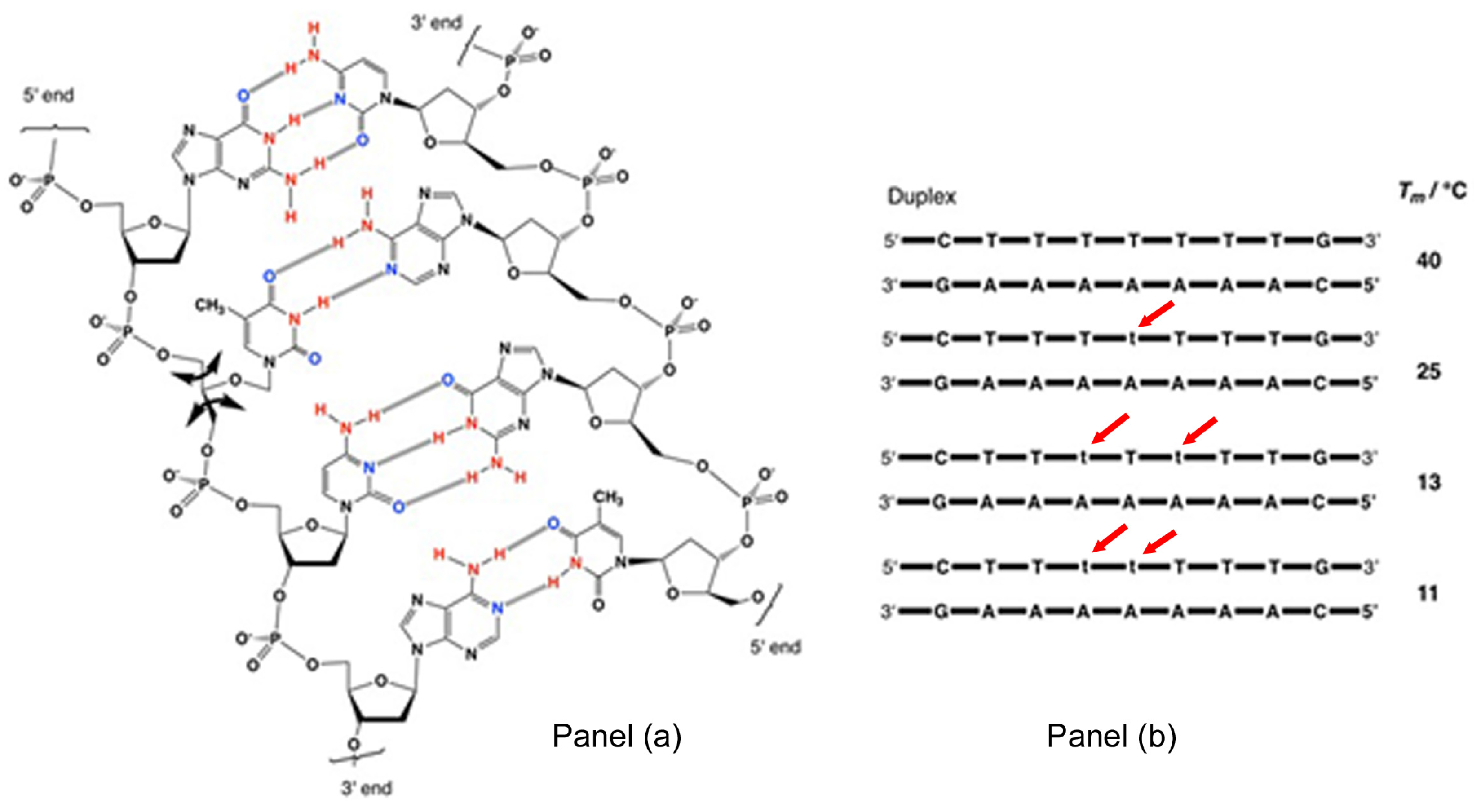



Life Free Full Text De Novo Nucleic Acids A Review Of Synthetic Alternatives To Dna And Rna That Could Act As Bio Information Storage Molecules Html



Www Mdpi Com 75 1729 10 12 346 Pdf
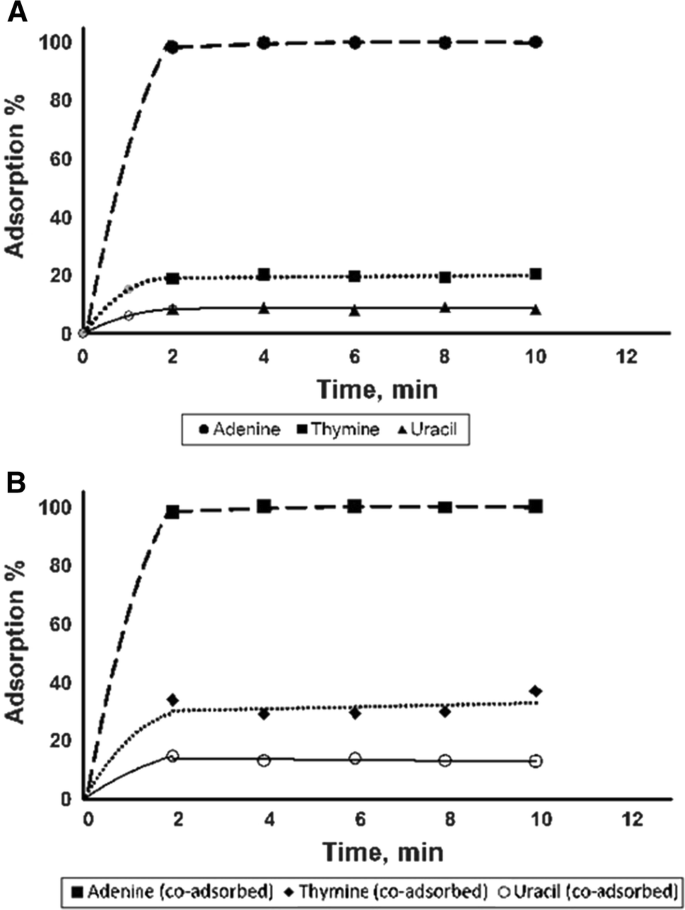



Radiolysis Of Adenine And Its Complementary Bases In Aqueous Solutions And Clay Suspensions Springerlink




Problem Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Par



1
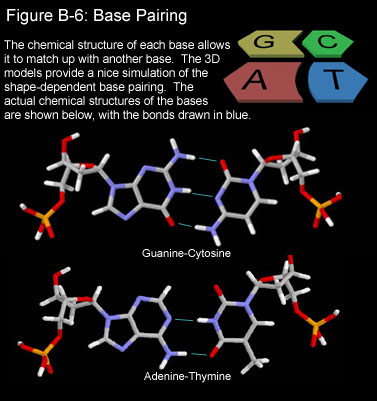



An Introduction To Dna And Chromosomes Text And Audio Hopes Huntington S Disease Information
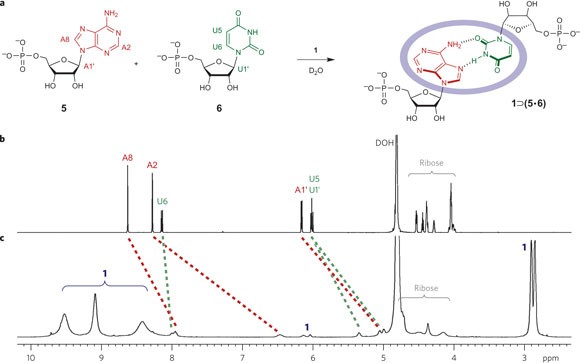



Minimal Nucleotide Duplex Formation In Water Through Enclathration In Self Assembled Hosts Nature Chemistry




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep
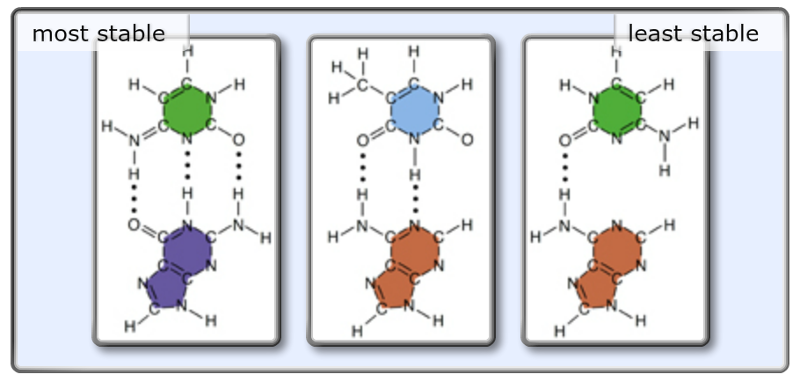



Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep
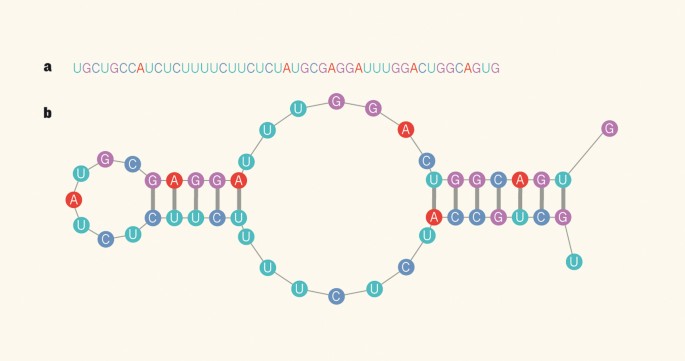



A Second Layer Of Information In Rna Nature




File Gc Dna Base Pair Svg Wikipedia



Shown In The Picture The Nucleotide Bases And Chegg Com



What Is The Complementary Base Pairing Rule
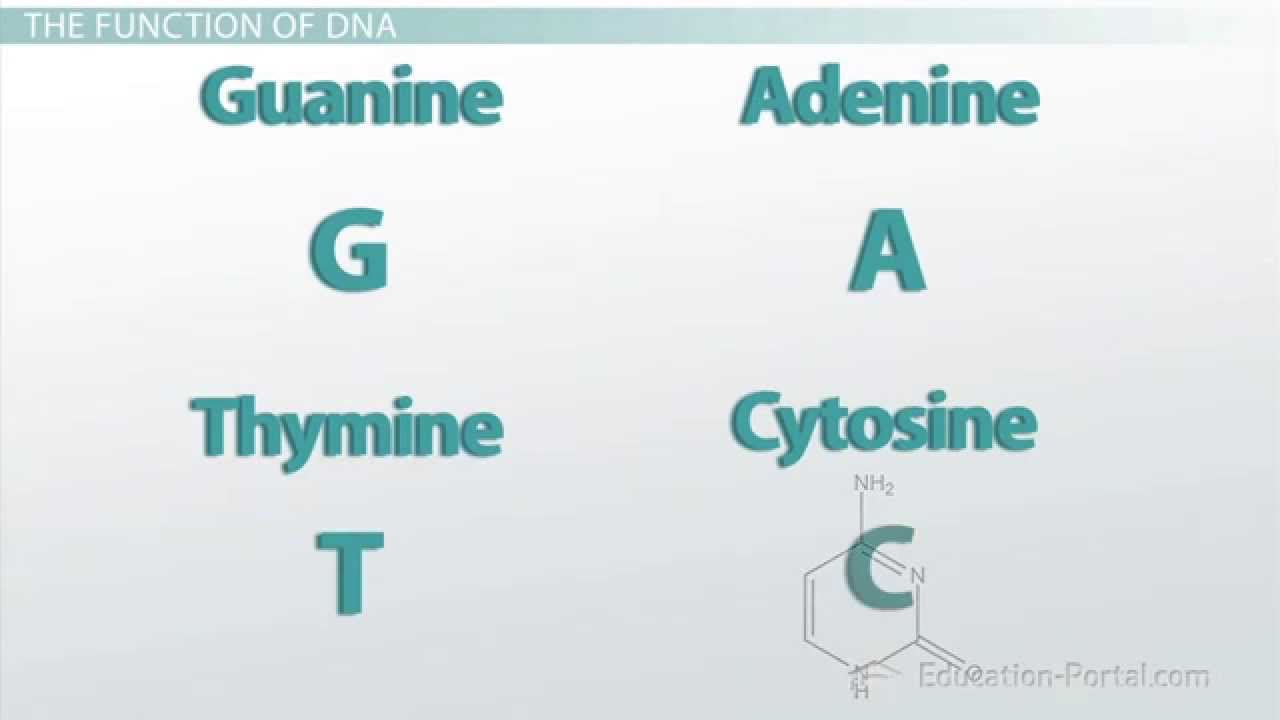



Dna Complementary Base Pairing Youtube




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners
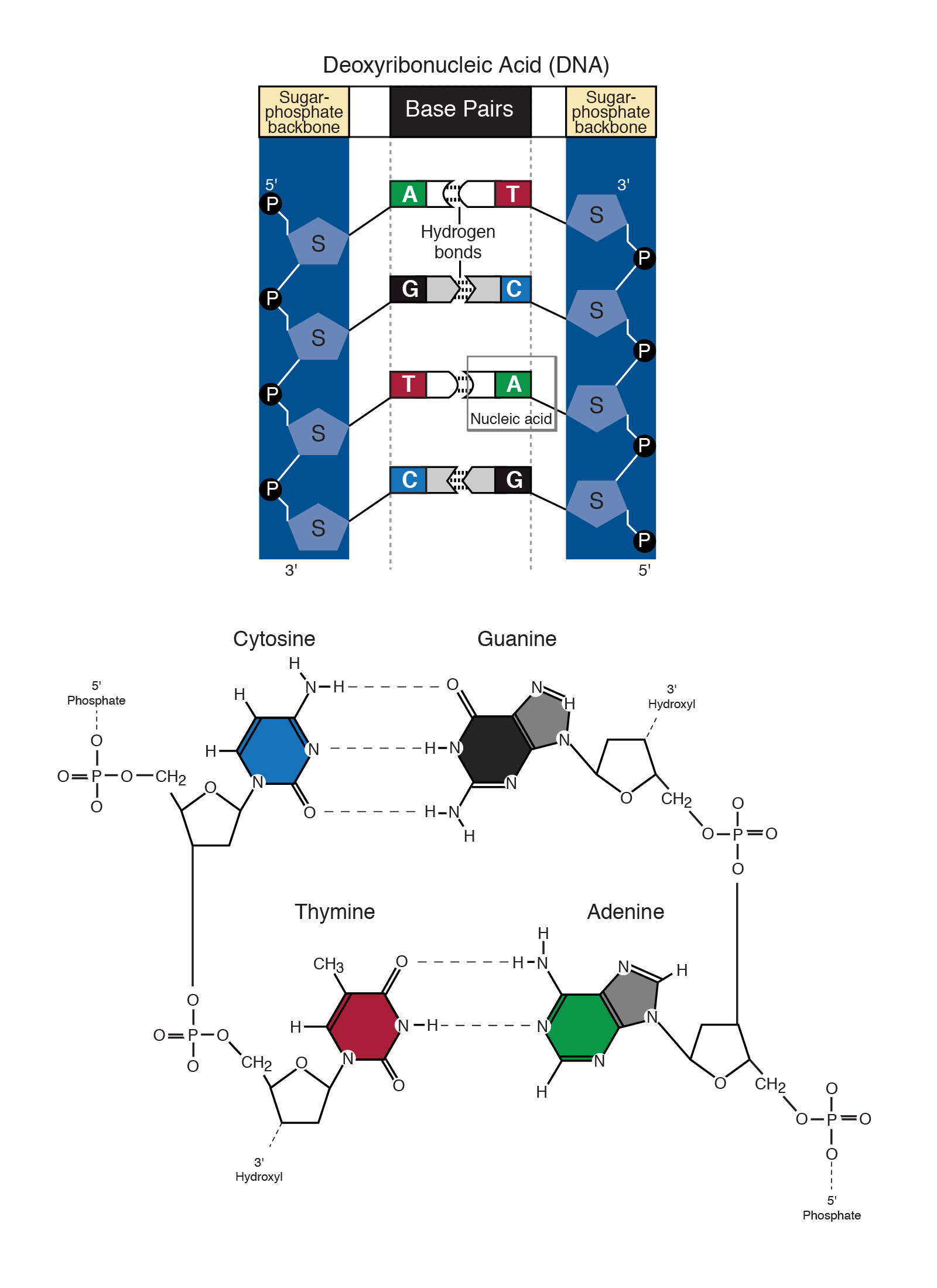



Base Pair




Bsc 10 Ch 16 17 18 Review Flashcards Quizlet




Hydrogen Bonding In Dna Base Pairs




A Model Of Proto Anti Codon Rna Enzymes Requiring L Amino Acid Homochirality Springerlink




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep
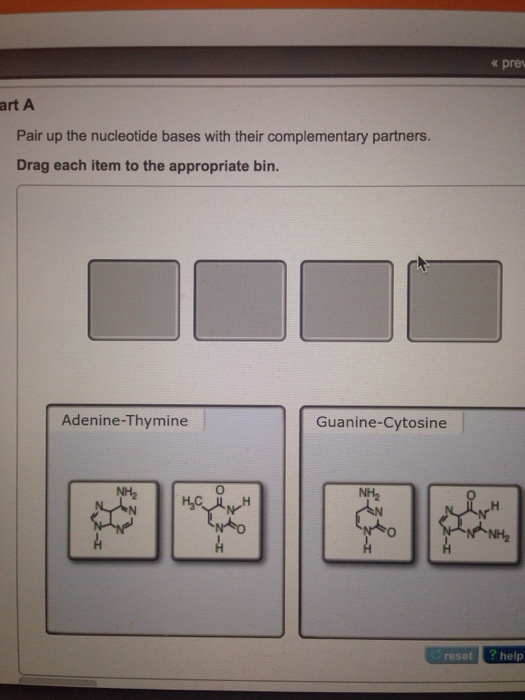



Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Chegg Com




Mb Ch 5 Pt 2 Adaptive Follow Up Set 3 Flashcards Quizlet
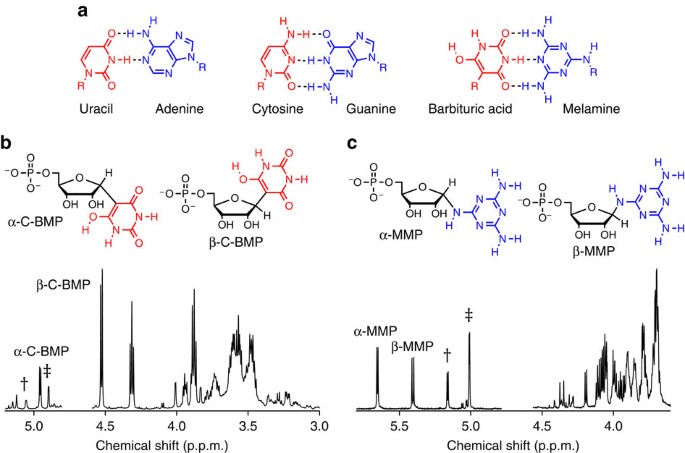



Spontaneous Formation And Base Pairing Of Plausible Prebiotic Nucleotides In Water Nature Communications




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners
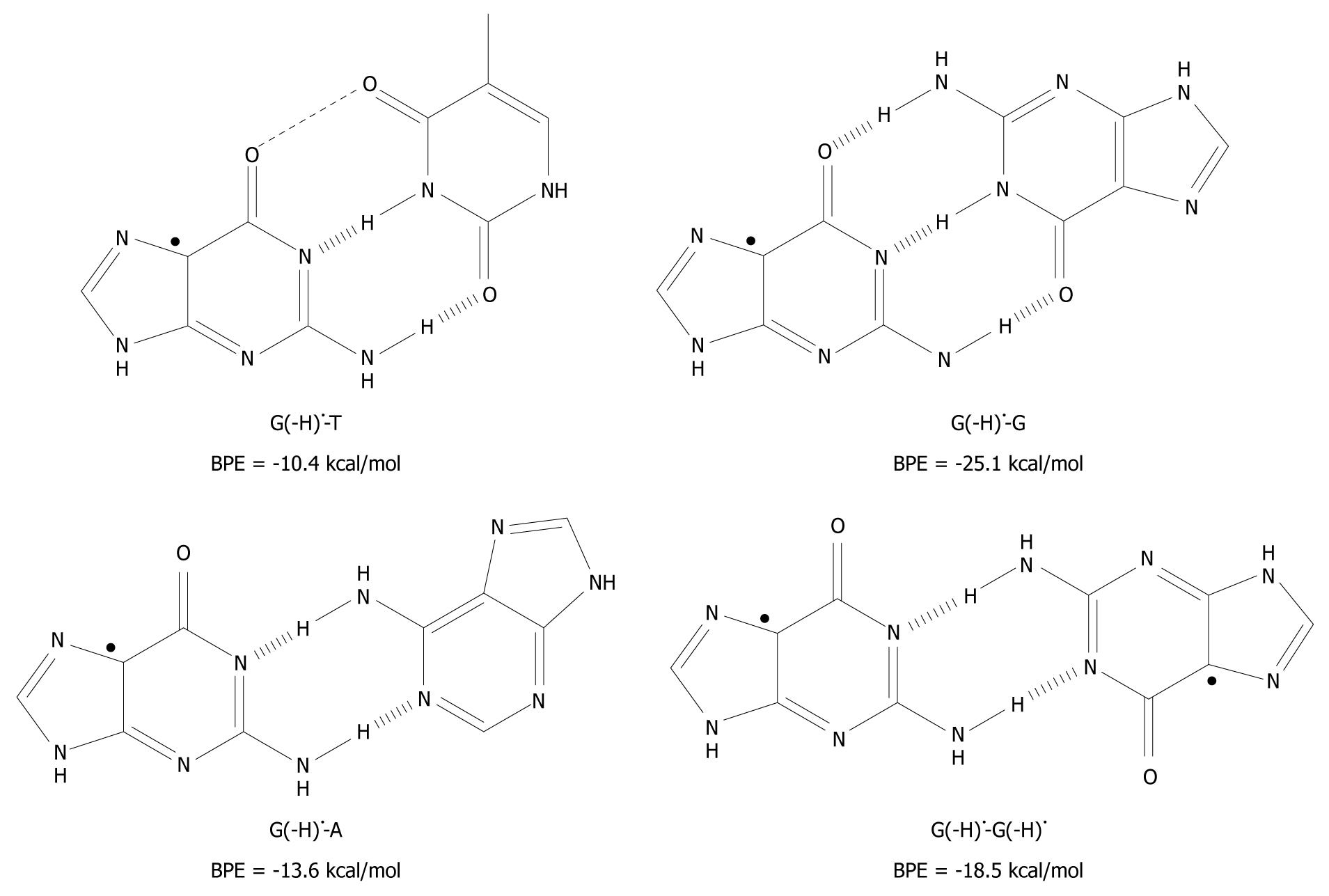



Molecular Mechanism Of Base Pairing Infidelity During Dna Duplication Upon One Electron Oxidation




Dna Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Complementary Base Pairing Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Complementarity Molecular Biology Wikipedia
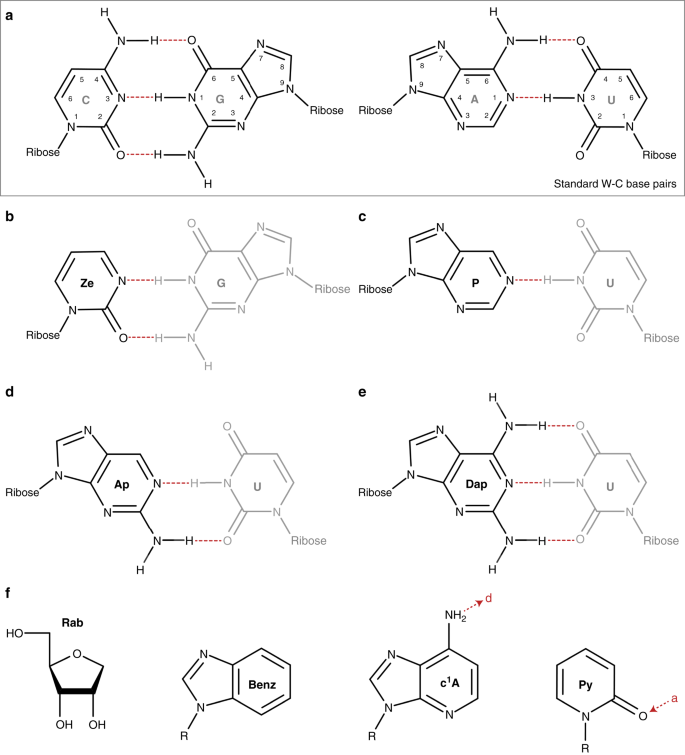



Translation Of Non Standard Codon Nucleotides Reveals Minimal Requirements For Codon Anticodon Interactions Nature Communications




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep




Life Free Full Text De Novo Nucleic Acids A Review Of Synthetic Alternatives To Dna And Rna That Could Act As Bio Information Storage Molecules Html



Blogs Glowscotland Org Uk Ea Public Scienceresources Uploads Sites 2108 19 01 Unit 1 Extended Response Questions And Marking Schemes Pdf




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep




Bsc 10 Ch 16 17 18 Review Flashcards Quizlet
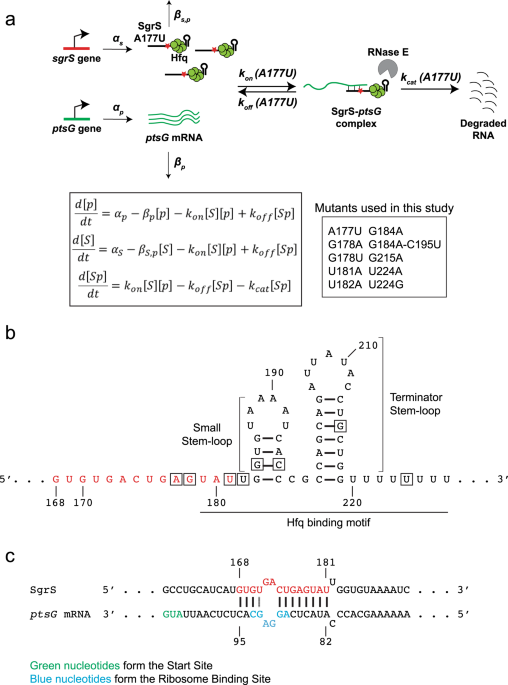



Effects Of Individual Base Pairs On In Vivo Target Search And Destruction Kinetics Of Bacterial Small Rna Nature Communications




Complementarity Molecular Biology Wikipedia
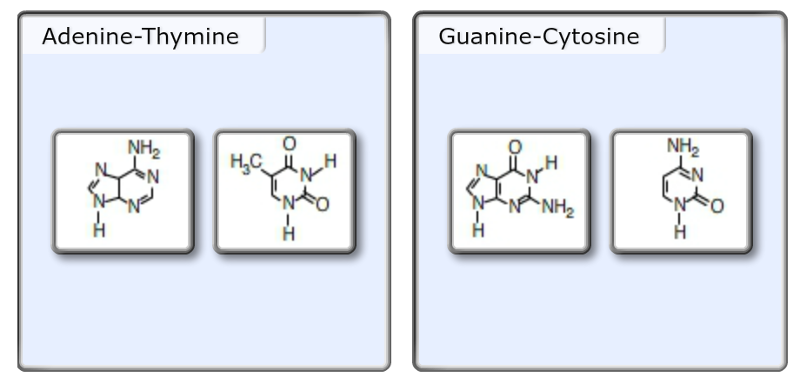



Print Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards
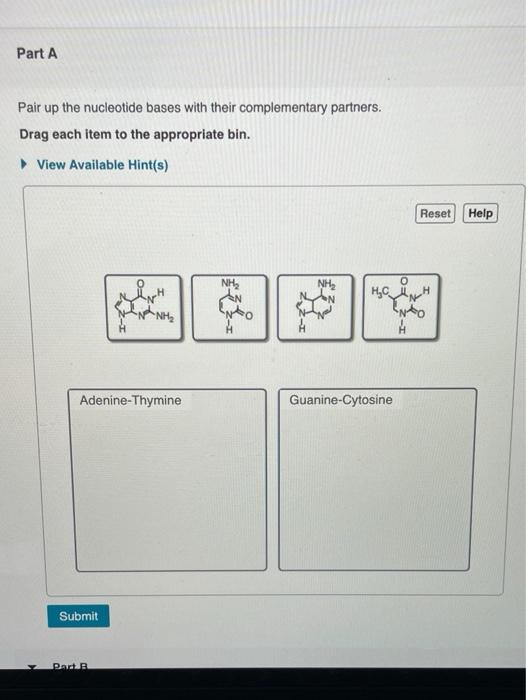



Reset Help Mrna Combines With Ribosome Amino Acids Chegg Com




Complementarity Molecular Biology Wikipedia




Dna Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Complementary Base Pairing Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




5 12 Png Part A Q 12 Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Drag Each Item To The Appropriate Bin View Available Hint S Reset Course Hero




Dna And Rna Part 2 Base Pair Dna




Nitrogenous Base An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Bsc 10 Ch 16 17 18 Review Flashcards Quizlet
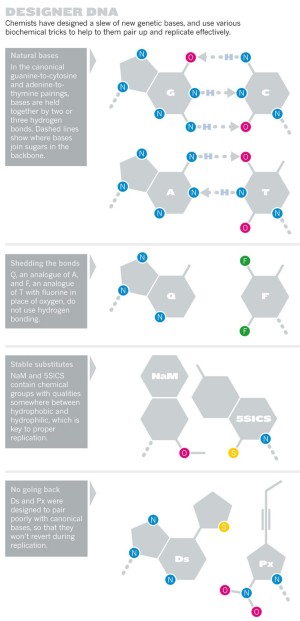



Chemical Biology Dna S New Alphabet Nature




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners




Complementarity Molecular Biology Wikipedia


